NumPy is a popular Python library created in 2005 by Travis Oliphant. It evolved from an earlier package called Numeric and has since become the foundation for scientific computing in Python. NumPy is widely used for handling arrays, performing mathematical operations, and supporting data analysis and machine learning tasks. Jobs like data scientists, Python developers, and machine learning engineers often depend on it. That is why NumPy interview questions are so common. In this blog, we cover the top 20+ questions with clear answers and tips to prepare.
Fun Fact: The name NumPy stands for “Numerical Python,” highlighting its core purpose of making numerical computing easier in Python.
Quick Facts About NumPy Interview

Note:
This blog on interview questions on NumPy covers a wide range of topics for both freshers and experienced professionals. You will also find questions for data analyst and data scientist roles, along with practical coding questions to help you prepare better.
NumPy Interview Questions for Freshers
Here are some commonly asked Python NumPy interview questions and answers for freshers and entry-level professionals.
- What is NumPy and why do data professionals use it?
NumPy is a Python library for numerical computing. It provides fast, efficient operations on arrays and matrices. Data professionals use it because it speeds up mathematical, statistical, and scientific calculations. It is the backbone for libraries like Pandas, SciPy, and scikit-learn.
- How do you create a 1D NumPy array from a Python list?
I can create a 1D array using np.array().
For example:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
This gives me a one-dimensional array with four elements.
- What are the main differences between a Python list and a NumPy array?
A Python list can store mixed data types. A NumPy array stores only one data type, which makes operations faster. NumPy arrays also consume less memory and allow vectorized operations, while lists rely on loops.
- How do you check the shape and number of elements in a NumPy array?
I can use .shape to check dimensions and .size for the total number of elements.
For example:
arr.shape # returns (rows, columns)
arr.size # returns total elements
- How can you reshape a NumPy array to a different dimension?
I can use the .reshape() method.
For example, converting a 1D array of 6 elements into a 2×3 matrix:
arr = np.arange(6).reshape(2,3)
- How do you select elements from a NumPy array using a condition (boolean indexing)?
I can pass a condition inside square brackets.
Example:
arr = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
arr[arr > 3] # returns [4,5]
- What is the difference between a view and a deep copy in NumPy?
| View in NumPy | Deep Copy in NumPy |
| Shares memory with the original array | Creates a new independent memory block |
| Faster, since no data is copied | Slower, as data is duplicated |
| Changes in view affect the original array | Changes do not affect the original array |
| Created using slicing or .view() method | Created using .copy() method |
| Useful for efficiency with large datasets | Useful when independent data is required |
NumPy Interview Questions for Experienced
These are advanced NumPy in Python interview questions that are commonly asked to experienced professionals.
- What is broadcasting in NumPy and how does it work?
Broadcasting lets arrays of different shapes interact in arithmetic operations. NumPy automatically stretches the smaller array along compatible dimensions without copying data. For example, adding a scalar to a 2D array adds the scalar to every element.
- How can you perform rolling window calculations (e.g. moving average) on an array?
I can use np.convolve() with a window of ones, divided by the window length. This produces a moving average. Another way is with sliding_window_view from NumPy, which creates rolling views that are more flexible for advanced use cases.
- Describe how to handle large arrays outside of memory using NumPy.
I can use memory-mapped files with np.memmap. It lets me access parts of large datasets on disk as if they were arrays in memory. This avoids loading the full dataset into RAM, which is useful for big data or scientific tasks.
- What is advanced indexing and how is it different from basic indexing?
Basic indexing uses slices and integers. Advanced indexing allows boolean masks, arrays of indices, or both. It always returns a copy, not a view, unlike slicing. For example, using an index list [0,2,4] selects specific elements from an array.
- How can you apply a function across rows or columns of a 2D array in NumPy?
I can use np.apply_along_axis() and pass the function with the axis parameter. Another approach is writing vectorized functions that naturally operate on entire rows or columns without loops.
- How do you implement a simple clustering algorithm like K-Means using only NumPy?
I would start by initializing random centroids. Then I would compute distances between points and centroids using np.linalg.norm. Each point is assigned to the closest centroid. The centroids are updated as the mean of their assigned points. The process repeats until convergence.
Also Read - Top 20+ Python Interview Questions for Data Analyst
NumPy Interview Questions for Data Analysts
Let’s go through important interview questions on NumPy in Python that recruiters ask when hiring for a data analyst role.
- How do you compute basic statistics, like mean, median, and standard deviation on a NumPy array?
I use built-in functions: np.mean(), np.median(), and np.std(). These functions are optimized and work directly on arrays, even with large datasets. They also accept an axis argument for column-wise or row-wise calculations.
- How can you normalize data (e.g. min-max scaling) using NumPy?
I subtract the minimum and divide by the range:
norm = (arr – arr.min()) / (arr.max() – arr.min())
This scales all values between 0 and 1.
For z-score normalization, I can use (arr – arr.mean()) / arr.std().
- What technique would you use to replace missing or infinite values in a NumPy array?
I detect them using np.isnan() and np.isinf(). Then I can replace values with np.nan_to_num() or by assignment.
For example:
arr[np.isnan(arr)] = arr.mean()
This is useful in cleaning datasets before analysis.
- How do you count occurrences of values efficiently in a NumPy array?
I use np.unique(arr, return_counts=True). It returns unique elements and their frequencies.
For integer data, np.bincount() is faster, as it directly counts how many times each index appears.
- How can NumPy be used to label data conditionally (e.g. using where)?
I apply np.where(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false).
Example:
labels = np.where(arr > 0, “Positive”, “Negative”)
This quickly creates labels without loops, which is especially helpful for preprocessing tasks in analytics.
Also Read - Top 35+ Data Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
NumPy Interview Questions for Data Scientists
Here are some commonly asked NumPy data science interview questions and their answers.
- How do you compute eigenvalues or perform linear algebra operations using NumPy?
I use the numpy.linalg module. For example, np.linalg.eig() computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors, while np.linalg.inv(), np.linalg.det(), and np.linalg.solve() handle inverses, determinants, and linear equation systems. These functions are optimized and widely used in statistical modeling.
- What is vectorization and how does it speed up computations?
Vectorization means replacing explicit Python loops with array operations. NumPy executes these operations in compiled C, making them much faster.
For example, adding two arrays with arr1 + arr2 runs far quicker than looping through elements.
- How do you memory-map a large dataset with NumPy to reduce memory use?
I use np.memmap(). It allows me to access large binary files stored on disk as arrays without loading them fully into memory. I can read slices of data when needed, which is essential for working with very large datasets in data science pipelines.
- Why is NumPy preferred over MATLAB or Octave for array operations in Python?
NumPy is open-source, integrates seamlessly with Python libraries, and supports a huge ecosystem for machine learning and analytics. It offers similar numerical performance but adds flexibility through Python’s general-purpose features. Data scientists often prefer NumPy because it fits directly into end-to-end workflows.
Also Read - Top 50+ Data Science Interview Questions and Answers
NumPy Coding Interview Questions
This section focuses on practical NumPy questions for interview that test your coding skills.
- Write code to flatten a multi-dimensional array into a 1D array.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
flat1 = a.ravel() # view when possible
flat2 = a.flatten() # always returns a copy
ravel() is fast and may return a view; flatten() always copies.
- How would you add a one-pixel (or one-element) border of zeros around a 2D array?
import numpy as np
A = np.ones((3, 4))
B = np.pad(A, pad_width=1, mode=”constant”, constant_values=0)
pad expands by one on all sides with zeros.
- Write a program to swap two axes of a NumPy array (transpose non-square matrix).
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(12).reshape(2, 3, 2) # shape (2,3,2)
B = np.swapaxes(A, 0, 1) # shape (3,2,2)
C = A.transpose(1, 0, 2) # same result as swapaxes(0,1)
swapaxes is explicit for two axes; transpose accepts a full permutation.
- How can you repeat each element of an array multiple times (e.g. 5 times)?
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
N = 5
out1 = np.repeat(arr, N) # [1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3]
# For 2D by columns or rows:
M = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
repeat_rows = np.repeat(M, 3, axis=0) # repeat rows
repeat_cols = np.repeat(M, 2, axis=1) # repeat cols
- Show how to convert a string array to uppercase or lowercase using NumPy character functions.
import numpy as np
s = np.array([‘i’, ‘love’, ‘NumPy’, ‘AND’, ‘interview’], dtype=str)
upper_ = np.char.upper(s)
lower_ = np.char.lower(s)
title_ = np.char.title(s)
swap_ = np.char.swapcase(s)
np.char methods operate element-wise on string arrays.
NumPy MCQs
Here are some quick NumPy multiple-choice questions to test your knowledge and prepare for interviews.
- NumPy stands for:
- A) Number Python
- B) Numerical Python
- C) Nobody Python
- D) None of the above
Answer: B) Numerical Python
- What does ndim report for a NumPy array?
- A) Number of dimensions
- B) Number of elements
- C) Memory size
- D) Data type
Answer: A) Number of dimensions
- Which method reshapes arrays?
- A) reshape()
- B) resize()
- C) transform()
- D) shape()
Answer: A) reshape()
- What function will fill an array with zeros?
- A) zeroes()
- B) zeros()
- C) fill_zero()
- D) create_zero()
Answer: B) zeros()
- What does itemsize provide?
- A) Number of elements
- B) Size in memory of each element
- C) Total memory footprint
- D) Number of bytes in array
Answer: B) Size in memory of each element
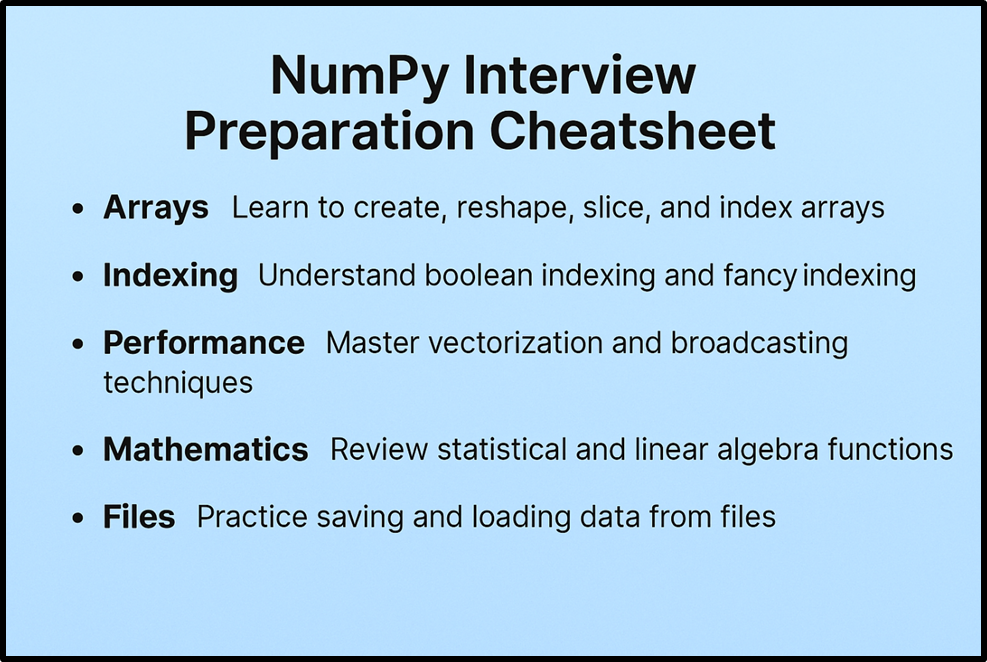
Tips to Prepare for NumPy Interview
NumPy is widely used in data science and strong fundamentals can boost interview success. Here are some tips to help you prepare:
- Revise array creation, slicing, reshaping, and broadcasting concepts
- Practice coding problems with real data instead of only theory
- Learn differences between lists and arrays with examples
- Focus on performance tricks like vectorization and memory mapping
- Solve mock interview questions regularly to build speed and confidence
- Practice the most asked NumPy interview questions
NumPy Interview Preparation Cheat Sheet
Wrapping Up
With these 20+ NumPy interview questions and answers, you now have a solid foundation to face both basic and advanced questions confidently. Keep practicing with real problems to sharpen your skills further.
If you are looking for IT jobs including roles that need NumPy, visit Hirist to find opportunities that match your career goals.
FAQs
According to AmbitionBox, the average annual salary for Python developers in India is around ₹6.4 Lakhs. The salary typically ranges between ₹1.9 Lakh to ₹11 Lakhs. The monthly in-hand salary usually falls around ₹32,000 – ₹33,000.
Python Developer salary overview
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual salary range | ₹1.9 Lakh – ₹11 Lakhs |
| Avg. annual salary | ₹6.4 Lakhs |
| Monthly in-hand salary | ₹32,000 – ₹33,000 |
| Experience range shown | 0 – 4 years |
Salary by experience
| Experience | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Fresher | ₹3.3 Lakhs per year |
| 1 year | ₹3.6 Lakhs per year |
| 2 years | ₹5.0 Lakhs per year |
| 3 years | ₹6.7 Lakhs per year |
Salary by city
| City | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Bangalore / Bengaluru | ₹6.7 Lakhs per year |
| Mumbai | ₹6.7 Lakhs per year |
| Chennai | ₹6.5 Lakhs per year |
| Gurgaon / Gurugram | ₹6.5 Lakhs per year |
| Pune | ₹6.5 Lakhs per year |
Companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta, IBM, and Accenture regularly hire candidates with strong NumPy skills, especially for data-related roles.
The process usually involves an online coding test, followed by technical interviews on Python, NumPy, and data structures, and finally a round on problem-solving or case studies.
Most companies conduct 3–5 rounds, including coding challenges, technical interviews, and one HR or behavioral round.
No. While NumPy is essential, you also need knowledge of Pandas, SQL, statistics, and machine learning basics to succeed in most data science interviews.

