Splunk is a powerful platform used to search, monitor and analyze machine data. It was founded in 2003 by Michael Baum, Rob Das and Erik Swan in San Francisco. The idea started as a way to make sense of messy log files that businesses often ignored. Over time, Splunk became popular in industries like finance, healthcare and IT for security, analytics and troubleshooting. Today, roles such as Splunk developer, administrator and architect are in demand. To help you prepare, here are the top 20+ Splunk interview questions and answers.
Fun Fact: Splunk is used by over 15,000 companies worldwide for data analysis and monitoring.
Note: In this blog, we are covering interview questions on Splunk for freshers, experienced professionals, developers, admins, architects, as well as scenario-based roles.
Splunk Interview Questions for Freshers
Here are the common Splunk interview questions and answers to help beginners understand the basics and get ready for their first interview.
- What is Splunk, and what problems does it solve?
Splunk is a platform that collects, indexes, and analyzes machine-generated data in real time. It helps organizations turn logs and events into meaningful insights. Common uses include monitoring, troubleshooting, and detecting security issues.

- Explain the main components of Splunk architecture.
Splunk has three key parts: Forwarder, Indexer, and Search Head. The Forwarder collects data from sources. The Indexer processes and stores that data. The Search Head allows users to search, create dashboards, and visualize results.
- What are Splunk Forwarders, and how are Universal and Heavy Forwarders different?
A Forwarder is a Splunk agent that sends data to an Indexer. A Universal Forwarder sends raw data with very little processing. It is lightweight and commonly used. A Heavy Forwarder parses and filters data before sending it, but it consumes more resources.
- What is a Splunk Indexer, and how does the indexing process work?
The Indexer transforms incoming raw data into events and stores them. It breaks data into buckets (hot, warm, cold, frozen) for better management. This process allows fast searching and reporting later.
- Name some common configuration files in Splunk and their purpose.
- props.conf: Defines source types and field extractions.
- indexes.conf: Sets up index storage details.
- inputs.conf: Configures data inputs.
- transforms.conf: Handles data filtering and routing.
- server.conf: Stores system-level settings.
- What are the differences between the Free and Enterprise versions of Splunk?
Splunk Free allows limited data indexing and lacks authentication, alerting, and distributed search. Splunk Enterprise supports large-scale indexing, user management, alerts, clustering, and advanced security features. Most organizations use the Enterprise version for production environments.
Splunk Interview Questions for Experienced
These Splunk interview questions are commonly asked to experienced professionals preparing for senior-level roles.
- What is the difference between Search Head Pooling and Search Head Clustering?
Search Head Pooling was an older method where multiple search heads shared configuration using shared storage. It is deprecated. Search Head Clustering is the modern approach. It provides replication, high availability, and consistency across search heads, making it reliable for enterprise setups.
- How does Splunk prevent duplicate indexing of logs?
Splunk uses a feature called the Fishbucket. This is a hidden index that stores file seek pointers and CRC values. It allows Splunk to track what portion of a file has been read already. This prevents re-indexing of the same data when inputs restart.
- What are Search Factor (SF) and Replication Factor (RF) in Splunk clustering?
Search Factor defines how many searchable copies of data are kept in the cluster. Replication Factor defines how many total copies of data exist across indexers. For example, RF=3 means three copies are stored, while SF=2 means at least two of them are searchable.
- Explain the role of the Splunk Dispatch Directory.
The Dispatch Directory is where Splunk temporarily stores search-related artifacts. Each running or completed search gets its own folder with search logs, results, and metadata. By default, these files are deleted after a set period, unless results are saved.
- What is Splunk SmartStore, and how does it optimize storage in large environments?
SmartStore separates compute from storage. Hot data stays on indexers for fast access. Warm and cold data move to remote object storage such as AWS S3 or Azure Blob. This reduces infrastructure costs while keeping frequently used data available quickly.
Splunk Scenario Based Interview Questions
Let’s go through important scenario-based interview questions on Splunk.
- A sudden spike in log ingestion exceeds the daily license limit. How would you troubleshoot it?
First, I would check the Splunk Monitoring Console to identify which source or index is consuming unexpected data. Next, I would filter out unnecessary logs at the forwarder using props and transforms. If critical, I’d reassign license pools or adjust retention to control usage.
- Your team needs to monitor containerized applications running on Kubernetes. How would you implement Splunk for this?
I would deploy Splunk Connect for Kubernetes, which collects logs, metrics, and metadata from pods and nodes. It integrates directly with the indexer or Splunk Observability Cloud. This provides insights into application health, container events, and cluster performance.
- A Splunk search query is running very slowly, what steps would you take to improve its performance?
I would first review the query with Job Inspector to see where time is spent. Then I’d refine search terms, avoid wildcards, and use indexed fields. Using summary indexing or data models can also improve speed for repeated searches.
- How would you configure Splunk to handle logs from a multi-cloud environment (AWS, Azure, GCP)?
I would use Splunk Add-ons for each cloud provider. These provide inputs for CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, or GCP Stackdriver logs. Then I’d centralize data in Splunk Enterprise or Cloud and normalize it with the Common Information Model for consistent analysis.
Splunk Admin Interview Questions
This section covers Splunk interview questions and answers for admin roles.
- How does data move through the bucket lifecycle (Hot, Warm, Cold, Frozen) in Splunk?
New data is stored in Hot buckets. When full, it rolls to Warm, which is still searchable but read-only. Later, data moves to Cold for long-term storage. Finally, it becomes Frozen, which is deleted or archived based on settings.
- What types of alerts can you create in Splunk, and how are they used in real-time monitoring?
There are two types: Real-time and Scheduled alerts.
Real-time alerts fire immediately when conditions are met, often used for security or downtime detection.
Scheduled alerts run at defined intervals, making them suitable for reports and routine monitoring.
- How do you manage user access and roles in a multi-tenant Splunk deployment?
I assign role-based access using Splunk’s authentication system. Separate indexes are created per tenant, and roles are mapped to specific data and dashboards. This keeps visibility and control clear.
Splunk Developer Interview Questions
These interview questions on Splunk are aimed at developers, focusing on building apps and customizing searches.
- What is SPL (Search Processing Language), and how is it used in queries?
SPL is Splunk’s query language. It allows searching, filtering, and transforming machine data. Developers use it to create dashboards, alerts, and reports from indexed logs.
- Explain the difference between the stats, eventstats, and transaction commands.
The stats command generates summary statistics and returns only aggregated results. eventstats is similar but appends those stats to each event for context. transaction groups related events into a single result, often used for sessions or multi-step processes.
- How would you use the timechart command to create a time-series visualization?
The timechart command converts data into time-based charts. For example, … | timechart count by status shows counts of events over time. It’s widely used to track trends, performance, or error spikes.
Splunk Architect Interview Questions
Here are the commonly asked Splunk interview questions for architect roles.
- What are the different deployment modes in Splunk (Standalone, Distributed, Clustered), and when do you use each?
Standalone is for small setups or testing where all roles run on one server. Distributed mode separates components across servers to handle larger volumes. Clustered mode adds redundancy and high availability, making it ideal for enterprise-scale workloads.
- How does Federated Search work, and why is it important in hybrid or multi-cloud setups?
Federated Search lets Splunk query multiple environments without moving data. It is critical in hybrid or multi-cloud setups where data may reside in AWS, Azure, or on-prem. This provides a single pane of analysis.
- What are the best practices for designing a scalable Splunk architecture for high-ingestion environments?
Distribute indexers for load, configure clustering, and use SmartStore for cost-effective storage. Plan role separation, monitor license usage, and design indexes carefully to maintain performance.
Splunk SIEM interview questions
Here are the common Splunk SIEM interview questions and answers.
- How is Splunk used as a SIEM tool?
Splunk collects logs from firewalls, servers, and applications, then correlates events to detect threats. With apps like Splunk Enterprise Security (ES), it provides dashboards, alerts, and incident investigation for security teams.
- What is notable event grouping in Splunk Enterprise Security?
Notable event grouping helps analysts by combining related security alerts into a single incident. This reduces alert fatigue and makes investigations faster since correlated events are reviewed together instead of one by one.
- How do you detect anomalies in user activity using Splunk?
I can create correlation searches on login attempts, access patterns, or unusual network activity. Splunk’s Machine Learning Toolkit also supports anomaly detection models, helping identify suspicious behavior beyond static rules.
Also Read - Top 25+ Incident Management Interview Questions and Answers
Splunk MCQs
Here are some Splunk MCQs you can practice before your interview.
- Which component in Splunk is responsible for storing and indexing data?
A. Forwarder
B. Indexer
C. Search Head
D. Deployment Server
Answer: B. Indexer
- Which command in Splunk is used to create time-series visualizations?
A. chart
B. timechart
C. stats
D. eval
Answer: B. timechart
- Which Splunk feature helps prevent duplicate indexing of logs?
A. SmartStore
B. Fishbucket
C. Federated Search
D. Metrics.log
Answer: B. Fishbucket
- What are the two types of Splunk Forwarders?
A. Heavy and Light
B. Standard and Premium
C. Universal and Heavy
D. Cold and Hot
Answer: C. Universal and Heavy
- In Splunk licensing, what does “Search Factor” mean?
A. Number of indexes
B. Number of searchable copies of data
C. Total amount of data ingested
D. User access limit
Answer: B. Number of searchable copies of data
Tips to Prepare for Splunk Interview
Preparing for a Splunk interview needs both technical knowledge and strong practical understanding. Follow these tips:
- Practice common Splunk interview questions with clear and simple answers
- Get hands-on with SPL queries and dashboards
- Learn key admin tasks like managing users and indexes
- Revise clustering concepts, licensing, and data lifecycle
- Work on real troubleshooting cases to explain step by step
Wrapping Up
With these 20+ Splunk interview questions and answers, you now have a solid foundation to prepare confidently for your next interview. Focus on both theory and hands-on practice, as employers look for real problem-solving skills.
Ready to put your knowledge to work? Find top IT openings, including Splunk jobs, on Hirist today.
FAQs
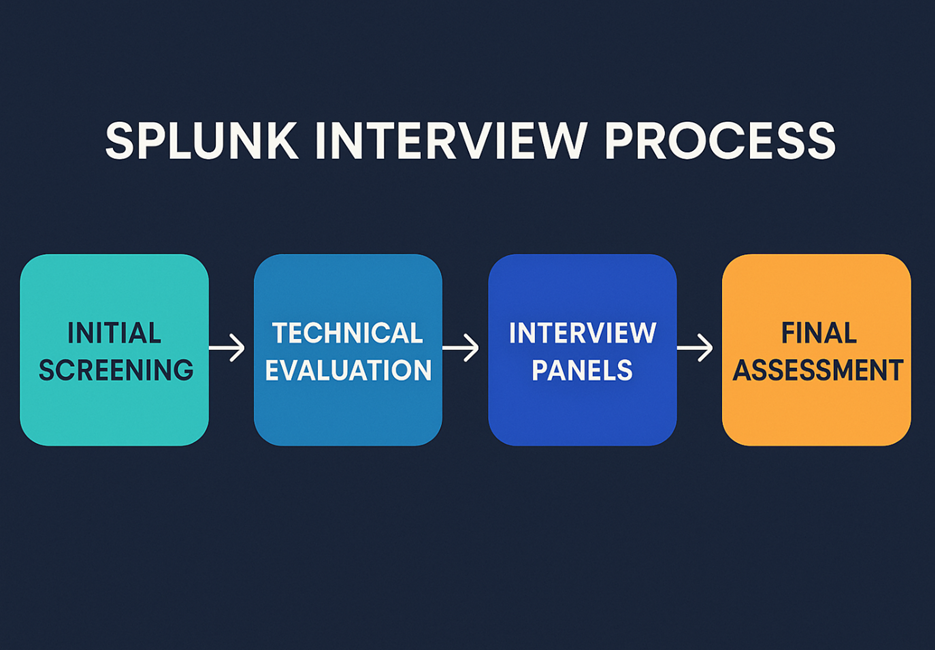
The process usually has four stages: initial screening, a technical round with scenario-based Splunk questions, an HR/managerial round to assess communication and fit, and then the final assessment.
Splunk is a platform for searching and analyzing machine data. It is used for monitoring, security, and analytics.
Forwarder, Indexer, and Search Head. The Forwarder collects data, the Indexer stores it, and the Search Head allows users to search and visualize results.
Forwarders are Splunk agents that send data to indexers. There are two types: Universal Forwarder and Heavy Forwarder.
According to AmbitionBox, Splunk Engineers in India earn between ₹4.8 Lakhs and ₹14.4 Lakhs annually. The average salary is around ₹7.7 Lakhs per year, which comes to an in-hand monthly salary of about ₹52,000–₹53,000.
Splunk Engineer Salary Overview (India, 2026)
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual salary range | ₹4.8 Lakhs – ₹14.4 Lakhs |
| Avg. annual salary | ₹7.7 Lakhs |
| Monthly in-hand salary | ₹52,000 – ₹53,000 |
| Experience range in data | 3 – 7 years |
Splunk Engineer salary based on experience:
| Experience | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| 3 years | ₹6.6 Lakhs per year |
| 4 years | ₹7.4 Lakhs per year |
| 5 years | ₹8.3 Lakhs per year |
| 6 years | ₹10.3 Lakhs per year |
Splunk Engineer salary based on location:
| City | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Noida | ₹18.0 Lakhs per year |
| New Delhi | ₹9.4 Lakhs per year |
| Gurgaon | ₹9.0 Lakhs per year |
| Pune | ₹8.5 Lakhs per year |
| Mumbai | ₹8.1 Lakhs per year |
Splunk Engineer salary at top companies:
| Company | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Wipro | ₹10.2 Lakhs per year |
| Capgemini | ₹9 Lakhs per year |
| Softsigniatech Solution | ₹8.6 Lakhs per year |
| Cognizant | ₹7.6 Lakhs per year |
| Mphasis | ₹7 Lakhs per year |
Firms like Amazon, Accenture, Infosys, Wipro, TCS, Deloitte, and Cisco actively hire Splunk developers, admins, and architects.

