Spring Security is a popular framework in the Spring ecosystem, introduced by Ben Alex in 2003. At first it was called Acegi Security but later it became Spring Security. The framework helps manage authentication, authorization, password protection, CSRF defense and access control in Java applications. It is trusted for securing enterprise projects and is a common skill for Java developers, backend engineers and security professionals. In this blog we share 25+ spring security interview questions and answers to help you get ready.
Fun Fact: Spring Security began as a side project by Ben Alex and later became part of the official Spring Framework due to its growing demand in enterprise Java applications.
Spring Security Interview Basics

Spring Security Interview Questions for Freshers
Here are some basic Spring Security interview questions that help beginners understand the core concepts and prepare for entry-level roles.
- What is Spring Security and how does it work?
Spring Security is a framework that provides authentication, authorization, and protection against common attacks. It works through a chain of servlet filters that process each request. Every request passes through these filters where the framework checks identity, roles, and permissions before granting access.
- What are the main components of the Spring Security architecture?
The main components of the Spring Security architecture are:
- AuthenticationManager: Central interface that handles authentication by delegating to multiple AuthenticationProviders.
- AuthenticationProvider: Performs the actual authentication logic, such as validating credentials against a database or LDAP.
- UserDetailsService: Loads user-specific data (username, password, roles) from a custom source like a database.
- SecurityContext: Holds authentication details of the current user, including principal and authorities.
- SecurityContextHolder: Provides access to the SecurityContext, usually stored in a ThreadLocal.
- Filter Chain: A chain of servlet filters (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter, CsrfFilter, etc.) that process authentication and authorization for every request.
- GrantedAuthority: Represents roles or permissions assigned to the user.
These components work together to authenticate users, authorize requests, and secure applications at both web and method levels.
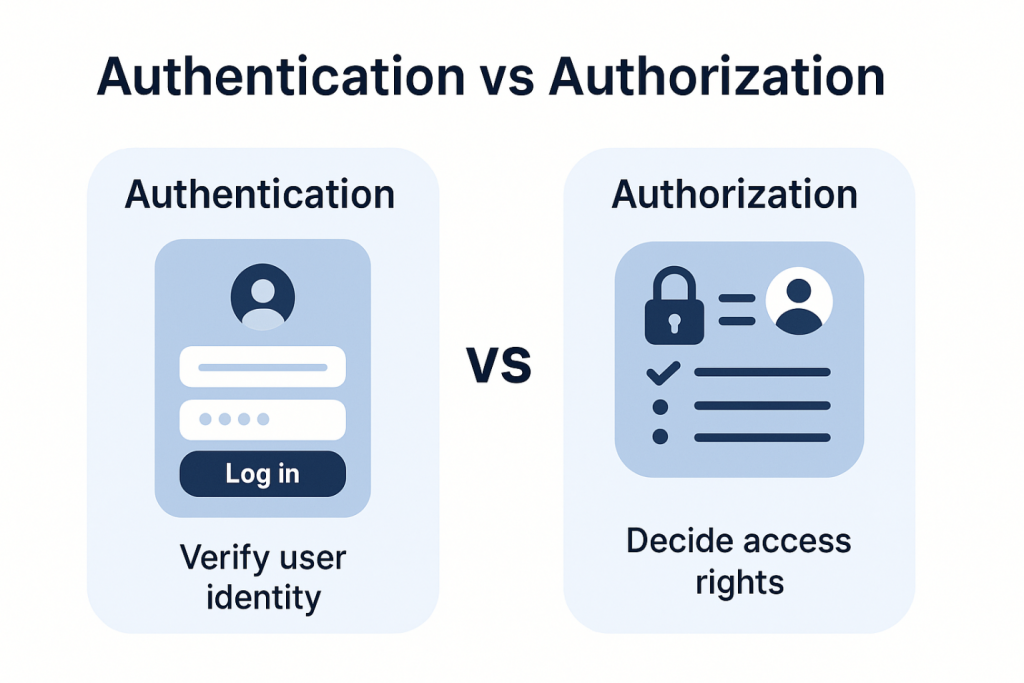
- What is authentication vs authorization in Spring Security?
Authentication is verifying the identity of a user, usually with a username and password. Authorization decides what resources the authenticated user can access.
| Aspect | Authentication | Authorization |
| Definition | Verifies the identity of the user | Decides what resources the user can access |
| Question Answered | Who are you? | What can you do? |
| Process | Validates credentials like username and password | Checks roles, authorities, and access rules |
| Stage | First step in security flow | Follows authentication |
| Example | User logs in with valid credentials | Only ADMIN can access /admin page, USER gets limited access |
| Spring Component | AuthenticationManager, UserDetailsService | AccessDecisionManager, annotations like @PreAuthorize |
- How do you configure Spring Security in a Spring Boot app?
To configure Spring Security in a Spring Boot application, start by including the spring-boot-starter-security dependency. By default, all endpoints are secured, so customization is done by defining a SecurityFilterChain bean. The HttpSecurity object is then used to specify access rules, roles, and authentication mechanisms.
Example:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers(“/admin/**”).hasRole(“ADMIN”)
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults()); // default login form
return http.build();
}
}
- What is the role of PasswordEncoder in Spring Security?
The PasswordEncoder in Spring Security is responsible for securing user passwords. It provides hashing algorithms like BCrypt or Argon2 so that plain text passwords are never stored in the database. During authentication, it compares the hashed version of the input password with the stored hash. This protects against attacks such as credential theft and makes password management safer in modern applications.
It is typically implemented by defining a PasswordEncoder bean:
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
- How does Spring Security protect against CSRF attacks?
CSRF protection is enabled by default. The framework generates a token for each session. This token is included in forms and verified on submission. If the token is missing or invalid, the request is blocked. This prevents attackers from forging requests.
- What is UserDetailsService and UserDetails used for?
UserDetailsService is an interface used to load user data by username. It returns a UserDetails object that holds information such as username, password, and roles. Applications often implement this to fetch user data from a database.
- Explain session management in Spring Security.
Spring Security controls sessions to stop attacks. It can migrate sessions on login to prevent fixation. It can limit how many sessions a user holds at once. It also handles timeouts to expire idle sessions. This keeps user interactions secure.
Also Read - Top 100+ Spring Boot Interview Questions
Spring Security Interview Questions for Experienced
Here are advanced Spring Security interview questions and answers for experienced professionals.
- What is AuthenticationManager and how is it used?
AuthenticationManager is the core interface for authentication in Spring Security. It takes an Authentication object and returns a fully authenticated one or throws an exception. It acts as the entry point for authentication logic.
Example:
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
public void login(String username, String password) {
Authentication auth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
Authentication result = authenticationManager.authenticate(auth);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(result);
}
- How does ProviderManager work and how does it delegate to AuthenticationProviders?
ProviderManager is the most common implementation of AuthenticationManager. It holds a list of AuthenticationProviders and tries them in sequence. If one provider can handle the authentication type, it processes it; otherwise, it passes it down the chain. This allows mixing providers like DAO authentication, LDAP, and JWT together.
- How does the Spring Security filter chain work?
Spring Security uses a chain of servlet filters to process requests. Each filter has a responsibility:
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter – Restores the SecurityContext.
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter – Handles login form authentication.
- BasicAuthenticationFilter – Handles HTTP Basic authentication.
- CsrfFilter – Protects against CSRF.
- ExceptionTranslationFilter – Catches exceptions and starts authentication if needed.
- FilterSecurityInterceptor – Makes the final authorization decision.
Requests pass through this chain in order, and filters can stop processing if access is denied.
- How do you secure method-level access using annotations like @PreAuthorize or @Secured?
Spring supports method-level security using annotations. In modern Spring Security (6+), it is enabled with:
@EnableMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
@Configuration
public class MethodSecurityConfig {}
Then annotate methods:
@PreAuthorize(“hasRole(‘ADMIN’)”)
public void deleteUser(Long id) { … }
@Secured(“ROLE_USER”)
public String getProfile() { … }
This enforces authorization before or after method execution.
- How do you customize security behavior using SecurityContext / SecurityContextHolder?
SecurityContext holds the authentication information for the current request. You can access or modify it directly:
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
String username = auth.getName(); // get logged-in username
Collection<?> roles = auth.getAuthorities(); // get roles
You can also programmatically set authentication (useful in custom login flows):
Authentication customAuth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(“user”, null, roles);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(customAuth);
- How do you configure custom authentication?
For database-backed authentication, you define a UserDetailsService and a PasswordEncoder:
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcUserDetailsManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
For LDAP, you configure an LdapAuthenticationProvider. For full custom logic, you can write your own AuthenticationProvider:
@Component
public class CustomAuthProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication auth) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = auth.getName();
String password = auth.getCredentials().toString();
// custom validation logic
if (“admin”.equals(username) && “pass”.equals(password)) {
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password, List.of(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(“ROLE_ADMIN”)));
}
throw new BadCredentialsException(“Invalid Credentials”);
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authType) {
return authType.equals(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}
Then you register it in your security configuration.
Advanced Spring Boot Security Interview Questions
This section covers Spring Security in Spring Boot interview questions that focus on practical scenarios and advanced configurations.
- How do you build a stateless authentication system for REST APIs using Spring Boot?
In a stateless setup, the server doesn’t keep sessions. Instead, tokens (often JWT) carry authentication details.
- Configure Spring Security to disable sessions:
http.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth.anyRequest().authenticated());
- Each request must include an Authorization header with a token.
- How do you integrate JWT (JSON Web Token) with Spring Boot and Spring Security?
JWT integration involves generating tokens after login and validating them on each request.
- Generate token after authentication using a library like io.jsonwebtoken.
- Add a custom filter that extracts and validates the token.
public class JwtAuthFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
String token = req.getHeader(“Authorization”);
if (token != null && token.startsWith(“Bearer “)) {
// validate token and set Authentication
}
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
}
Register the filter before UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.
- How do you refresh or revoke a JWT token in Spring Boot?
Refresh: Use a short-lived access token and a long-lived refresh token. Expose an endpoint (/refresh) to issue a new token when refresh token is valid.
Revoke: Since JWTs are stateless, you can’t invalidate them easily. Common approaches:
- Maintain a token blacklist in DB/Redis and check against it.
- Rotate signing keys so old tokens become invalid.
- How do you configure CORS and CSRF for secured APIs in Spring Boot?
For REST APIs:
- CORS: Allow trusted domains only.
http.cors(cors -> cors.configurationSource(request -> {
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
config.setAllowedOrigins(List.of(“https://trusted.com”));
config.setAllowedMethods(List.of(“GET”,”POST”));
return config;
}));
- CSRF: Disable CSRF for stateless APIs since tokens already provide protection.
http.csrf().disable();
- How do you implement a custom filter in Spring Security and place it in the filter chain?
Create a filter by extending OncePerRequestFilter. Add your custom logic (e.g., logging, header validation, token parsing).
@Component
public class CustomHeaderFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
String header = req.getHeader(“X-API-KEY”);
if (“secret”.equals(header)) {
chain.doFilter(req, res);
} else {
res.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
}
}
}
Register it in the chain:
http.addFilterBefore(customHeaderFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
Also Read - Top 50+ REST API Interview Questions and Answers
Other Important Spring Security Interview Questions
Now, we will cover additional Spring Security interview questions that are commonly asked across different roles and experience levels.
Java Spring Security Interview Questions
- How does Spring Security integrate with plain Spring web apps?
- How do you configure security in a Spring MVC environment?
- What is AbstractSecurityInterceptor and what role does it play?
- What is method security in Spring?
- What is the difference between DelegatingFilterProxy and FilterChainProxy in Spring Security?
Spring Security JWT Interview Questions
- What is a JWT and how is it structured?
- How do you sign and verify a JWT in Spring Security?
- How do you include roles or claims in a JWT and use them for authorization?
- How do you handle token expiration and refresh tokens?
- How do you protect against JWT replay or misuse?
OAuth 2 Spring Boot Interview Questions
- What are common OAuth2 grant types?
- How does the Authorization Code grant flow work in Spring Boot with Spring Security?
- How do you configure a resource server and authorization server in Spring Boot?
- How do you handle scopes, roles, and claims with OAuth2 in Spring Boot?
- How do you perform token introspection or validation in a Spring Boot resource server?
Spring Security MCQs
Let’s go through some multiple-choice spring security interview questions to quickly test your knowledge.
- Which annotation supports using SpEL expressions for access control?
A) @Secured
B) @PreAuthorize
C) @RolesAllowed
D) @Transactional
Answer: B) @PreAuthorize
- Which filter is responsible for restoring the SecurityContext for each request?
A) SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
B) UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
C) AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
D) CsrfFilter
Answer: A) SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- What does http.sessionManagement().sessionFixation().migrateSession() do?
A) Disables session fixation protection
B) Validates session on each request
C) Creates a new session after authentication
D) Invalidates user sessions
Answer: C) Creates a new session after authentication
- In Spring Boot with default settings, how is insecure HTTP access handled?
A) All endpoints are open
B) All endpoints require authentication
C) Only /login is protected
D) Static resources are blocked
Answer: B) All endpoints require authentication
- What does @EnableWebSecurity do?
A) Enables global method security
B) Enables web security configuration
C) Disables CSRF protection
D) Installs OAuth2
Answer: B) Enables web security configuration
- Which interface is used to load user-specific data for authentication?
A) UserDetails
B) UserDetailsService
C) AuthenticationProvider
D) PrincipalExtractor
Answer: B) UserDetailsService
- Which matcher should go first in antMatchers for correct security?
A) The most general
B) The least specific
C) The most specific
D) Order doesn’t matter
Answer: C) The most specific
How to Prepare for Spring Security Interview?
Preparing for a Spring Security interview needs focus on both core concepts and practical coding skills. Here are tips you can follow:
- Learn authentication, authorization, CSRF, CORS, and session management with clear examples.
- Practice configuring Spring Security in Spring Boot using SecurityFilterChain and custom filters.
- Revise JWT integration, token validation, and OAuth2 flows with hands-on projects.
- Review commonly used annotations like @PreAuthorize, @Secured, and method-level security.
- Be ready to explain the filter chain order and its importance.
- Solve mock questions and write short code snippets without relying only on theory.
Wrapping Up
So, these are the 25+ Spring Security interview questions and answers that can help you prepare better. Knowing both theory and practical code examples will make you confident in interviews. Keep practicing with real projects and review key concepts regularly.
Looking for IT jobs including Spring Security job roles? You will find the best opportunities on Hirist.
FAQs
Spring Boot Security interview questions can be challenging because they test both core concepts and practical coding, but steady practice with real examples makes them manageable.
For professionals with 10 years of experience, interviewers focus on advanced security design and real-world problem solving. Here are the common questions:
How do you design a scalable, stateless security architecture for microservices in Spring Boot?
How do you implement and secure OAuth2 resource servers and authorization servers in distributed systems?
What strategies do you use for token revocation, refresh, and key rotation in JWT-based security?
How do you integrate Spring Security with third-party identity providers like Keycloak or Okta?
How do you perform security audits, logging, and monitoring in Spring Boot applications at scale?
You can find Spring Boot Security interview questions and answers for experienced professionals in this blog, where we have covered advanced topics. You will also find detailed questions and answers on AmbitionBox, a trusted platform for interview preparation.
Expect questions about authentication mechanisms, role-based access, JWT, OAuth2, password encoding, CSRF protection, and securing REST APIs.
Leading firms like TCS, Infosys, Accenture, Capgemini, Cognizant, JP Morgan, and product companies hire professionals skilled in Spring Boot Security.
The process usually includes an online coding test, one or two technical rounds focusing on Spring Security and system design, followed by an HR discussion.

