Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced AI systems built to understand and generate human-like text. The roots go back to early natural language processing research, but modern LLMs gained attention after OpenAI introduced GPT models created by Sam Altman’s leadership. Today, LLMs power chatbots, coding assistants, content tools, and more. Companies hire roles like data scientists, AI engineers, and machine learning specialists to work with them. If you are preparing for such roles, practicing LLM interview questions is the smartest way to get ready. This blog covers the top 25 questions with clear and simple answers.
Fun Fact: About 67% of companies worldwide are using generative AI tools powered by large language models (LLMs). That represents roughly 201 million organizations.
LLM Interview Facts

Basic LLM Interview Questions
Here are some of the most common large language models interview questions that beginners are likely to face when preparing for roles in AI and machine learning.
- What is a Large Language Model and how is it trained?
A Large Language Model (LLM) is an AI system trained on massive text datasets to understand and generate human-like language.
Training involves two main stages: pre-training on general data to learn patterns of language, followed by fine-tuning on task-specific data. This process uses billions of parameters and advanced hardware to capture grammar, facts, and reasoning.
- How does the transformer architecture work?
The transformer uses self-attention to look at relationships between words in a sequence. Instead of reading text step by step like RNNs, it processes all tokens in parallel.
This makes transformers much faster and better at capturing long-range context. The architecture has encoder-decoder layers, multi-head attention, and feed-forward networks.
- What role does the context window play in LLM performance?
The context window defines how much text the model can consider at one time. A larger context window allows the model to remember longer conversations or documents.
In 2026, advanced models support windows up to hundreds of thousands of tokens. This makes them capable of analyzing books, long reports, and complex chats.
- How do LLMs handle out-of-vocabulary words or tokens?
They use subword tokenization methods like Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) or SentencePiece. These break unknown words into smaller pieces the model has seen before. This way, even new or rare words can be understood and generated accurately.
- What are common pre-training objectives like masked and autoregressive modeling?
Masked language modeling hides random words and trains the model to predict them, like BERT. Autoregressive modeling predicts the next token step by step, like GPT. Both help the model learn patterns, context, and semantics at scale.
- What is fine-tuning and when is it used?
Fine-tuning takes a pre-trained LLM and adapts it to a smaller, specific dataset. I would use it for tasks like legal text analysis, healthcare records, or customer support bots.
- Why can bias and fairness be a concern in LLM outputs?
Because models learn from human-written text, they sometimes pick up stereotypes or harmful associations. These biases can appear in answers or generated text, so monitoring and mitigation are critical in real applications.
Also Read - Top 90+ Machine Learning Interview Questions and Answers
Intermediate LLM Interview Questions
These large language models interview questions focus on deeper concepts and practical applications that intermediate-level candidates often face.
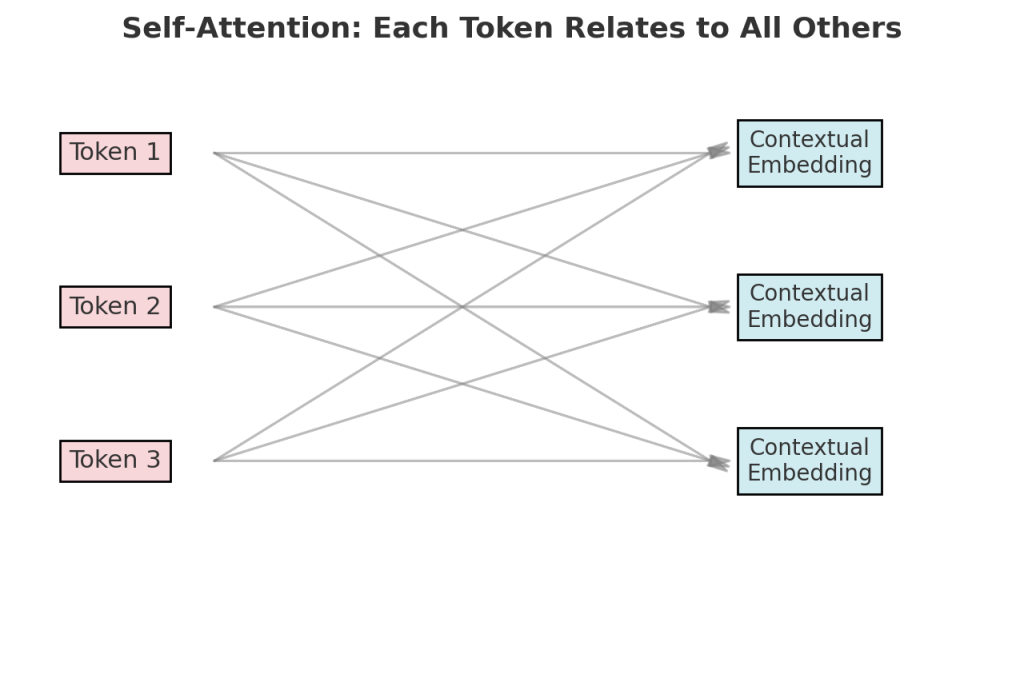
- What is self-attention and how does it work in a transformer?
Self-attention allows the model to weigh relationships between words in a sequence. Each token compares itself with every other token. This helps the model capture context across long text. It is the core reason transformers outperform older architectures.
- Why is tokenization critical for LLM inputs?
Tokenization breaks raw text into units like words or subwords. Without it, the model cannot process text effectively. Subword tokenization, such as BPE, helps handle rare or unseen words. This step directly affects accuracy and model performance.
- What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and how does it help?
RAG combines a retriever with a generator. The retriever finds relevant documents, and the generator uses them to create accurate answers. This method reduces hallucinations and brings in up-to-date or domain-specific information.
- How can you measure LLM performance using metrics like BLEU, ROUGE, or reference-free evaluation?
BLEU measures overlap with reference translations, often used in translation tasks. ROUGE compares recall and precision, useful for summarization. More recently, reference-free methods like LLM-as-a-judge are used. These rely on another strong model to evaluate outputs.
- How can reasoning ability in LLMs be improved through prompting?
Prompting techniques like chain-of-thought guide models to explain steps before answering. Few-shot prompts add examples to teach reasoning patterns. In interviews, I would highlight that prompt quality often shapes reasoning performance.
- What is a hallucination in LLM outputs, and how can it be addressed?
A hallucination happens when the model generates content that is wrong but looks correct. To control it, I would use RAG, better prompting, or rule-based checks. In production, human review is also common for sensitive use cases.
- What are some common decoding strategies (like beam search) and why are they used?
Decoding strategies shape how text is generated. Greedy decoding picks the highest probability token each step, but it can be repetitive. Beam search explores multiple possibilities for better results. Top-k and nucleus sampling balance creativity with relevance.
Advanced LLM Interview Questions
Let’s go through some challenging llm interview questions that assess advanced knowledge. Experienced professionals applying for senior roles often face these questions.
- What is few-shot learning and what makes it useful?
Few-shot learning allows an LLM to adapt to a new task with just a few examples. Instead of retraining, the model learns the task from the prompt itself. This saves time, reduces data needs, and makes models more flexible in real-world use.
- How do reasoning language models differ from standard LLMs?
Reasoning-focused models are trained or fine-tuned to handle logic-heavy tasks. They can solve math problems, code debugging, or multi-step queries more reliably. Standard LLMs may provide fluent answers, but reasoning models are better at structured problem-solving.
- What is Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and why is it important for LLM safety?
RLHF trains models using human feedback to prefer safe, accurate responses. It reduces harmful or biased outputs and makes LLMs more reliable for real-world use. In 2026, most advanced LLMs apply RLHF or DPO for safety alignment.
- What challenges can fine-tuning introduce, such as misalignment or harmful behavior?
Fine-tuning on narrow datasets may make the model lose general knowledge. This is called catastrophic forgetting. It can also pick up new biases if the dataset is unbalanced. In sensitive fields like healthcare or law, I would carefully test outputs before deployment.
- How does model degradation happen over time, and what’s a common way to address it?
Models degrade when real-world data shifts from the training distribution. For example, financial news or regulations change regularly. A common fix is periodic retraining or incremental updates with fresh data. Monitoring performance metrics helps catch drift early.
- What capabilities do models like Anthropic’s Claude 4 bring to reasoning tasks?
Claude 4 and similar 2025 models extend context length, making them handle huge documents. They also improve on safety and reasoning benchmarks. These advances mean fewer hallucinations, stronger reliability, and more usable outputs in enterprise settings.
LLM MCQs
Here are multiple-choice questions on LLMs to quickly test your understanding of key concepts and practical applications.
- Which mechanism allows transformer models to look at all tokens at once?
A) Recurrence
B) Self-attention
C) Convolution
D) Batching
Answer: B) Self-attention
- What is the main advantage of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
A) Faster token generation
B) Access to up-to-date or domain-specific data
C) Reduces model size
D) Eliminates need for fine-tuning
Answer: B) Access to up-to-date or domain-specific data
- Few-shot learning is useful because it:
A) Requires many examples
B) Needs no examples
C) Works with minimal examples
D) Only works after full training
Answer: C) Works with minimal examples
- What issue arises when an LLM produces confident but incorrect statements?
A) Generalization
B) Overfitting
C) Hallucination
D) Tokenization error
Answer: C) Hallucination
- What evaluation metric compares generated text to reference text using n-gram overlap?
A) Self-attention
B) BLEU
C) RAG
D) Few-shot
Answer: B) BLEU
How to Prepare for LLM Interview?
Preparing for an LLM interview takes knowledge of models and practical problem-solving skills. Here are some tips to help you prepare:
- Review basics like transformers, tokens, context windows, and embeddings
- Practice coding tasks with Python and PyTorch
- Study prompt engineering and RAG case studies
- Revise fine-tuning, bias, and fairness issues
- Be ready to explain evaluation metrics
- Practice explaining complex ideas in simple words
- Stay updated with latest model trends and research
Also Read - Top 45+ Artificial Intelligence (AI) Interview Questions and Answers
LLM Interview Cheat Sheet
Wrapping Up
So, these are the 25 LLM interview questions and answers that can help you prepare with confidence. Focus on understanding concepts, practicing problem-solving, and staying updated with the latest model trends. With the right preparation, you can do well in your next interview.
Looking for job opportunities in this field? Visit Hirist to find the best and highest-paying IT jobs, including exciting LLM job roles.
FAQs
In interviews, LLM usually refers to Large Language Models. These are advanced AI models like GPT or Claude, trained on massive datasets to generate and understand text. Interviewers may test your knowledge of their architecture, training, and applications.
The process usually includes a mix of technical interviews, coding assessments, system design discussions, and applied case studies like prompt engineering or RAG. Soft skills such as communication and problem-solving are also tested.
Show strong fundamentals, but also give examples from real projects. Be ready to explain trade-offs in design, address challenges like hallucination or bias, and demonstrate curiosity about emerging trends.
According to AmbitionBox, salaries for professionals working with AI and LLMs vary by role. Artificial Intelligence Engineers in India earn between ₹3 Lakhs to ₹32 Lakhs annually, with an average salary of ₹18.4 Lakhs.
Machine Learning Engineers, who often work closely with LLM systems, earn between ₹3.5 Lakhs to ₹25 Lakhs annually, averaging ₹11.4 Lakhs.
Machine Learning Engineer salary
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual salary range | ₹3.5 Lakhs – ₹25 Lakhs |
| Avg. annual salary | ₹11.4 Lakhs |
| Monthly in-hand salary | ₹55,000 – ₹57,000 |
| Experience range shown | 1 – 6 years |
Artificial Intelligence Engineer salary
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual salary range | ₹3 Lakhs – ₹32 Lakhs |
| Avg. annual salary | ₹18.4 Lakhs |
| Monthly in-hand salary | ₹66,000 – ₹67,000 |
| Experience range shown | 0 – 8 years |
Companies like Google, Microsoft, Meta, OpenAI, Anthropic, and NVIDIA are actively hiring. Many Fortune 500 firms also need LLM specialists for finance, healthcare, and enterprise solutions.

