The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) is a globally recognized certification by Cisco, founded in 1984 by Leonard Bosack and Sandy Lerner. It focuses on networking fundamentals, routing, switching, and security. Over the years, CCNA has become one of the most popular certifications for IT professionals looking to start or grow their careers in networking. From network engineers to system administrators, many roles require CCNA knowledge. In this blog, we cover the top 25+ CCNA interview questions and answers to help you prepare easily.
Fun Fact: Cisco has issued over 1 million CCNA certifications worldwide. This makes it one of the most popular networking certifications globally.
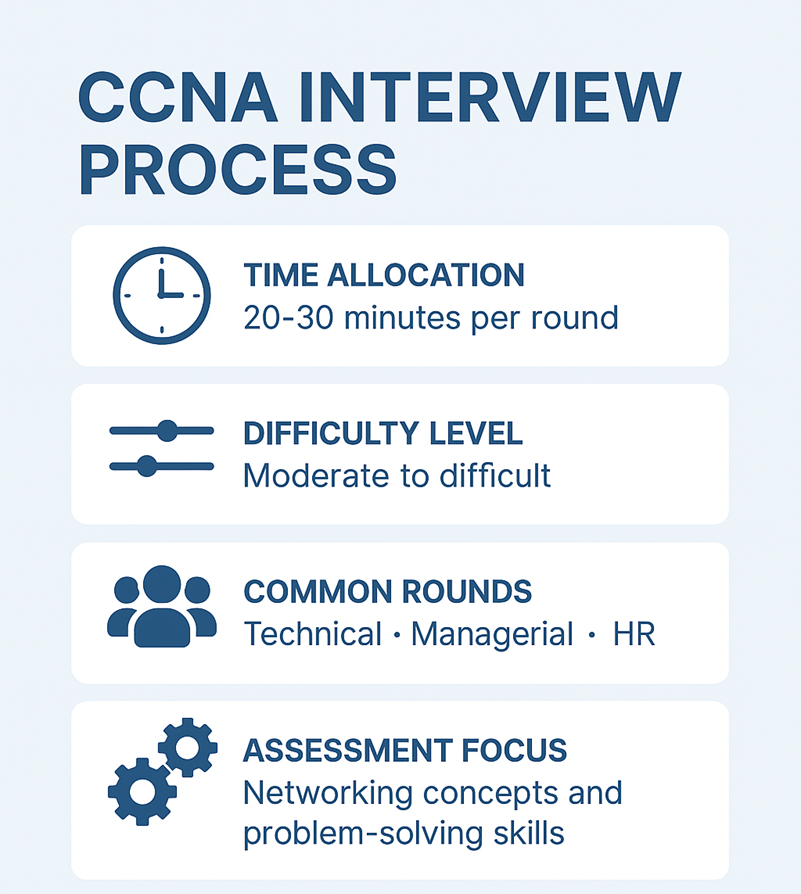
Basic CCNA Interview Questions
Here are some of the most common CCNA basic interview questions that beginners are often asked during networking job interviews.
- What is routing?
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network. Routers examine destination IP addresses and decide the best route to forward packets. They use routing tables and protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, or BGP. Routing is critical for connecting multiple networks and directing data efficiently.
- What is the purpose of the Data Link layer?
The Data Link layer, the second layer of the OSI model, handles node-to-node communication. It organizes data into frames, adds MAC addresses, and manages error detection. It also controls how devices access the physical medium. In short, it makes communication between two directly connected devices reliable.
- What does the LLC sublayer do?
The Logical Link Control (LLC) sublayer sits above the MAC sublayer in the Data Link layer. It provides flow control, multiplexing, and optional error correction. It allows multiple protocols (like IPv4 and IPv6) to share the same network medium without interference.
- What is MTU?
MTU stands for Maximum Transmission Unit. It defines the largest size of a packet that can be transmitted over a network. On Ethernet, the default MTU is 1500 bytes. Setting the MTU correctly helps avoid fragmentation and improves transmission efficiency.
- What is CDP?
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on Cisco devices. It gathers information about directly connected Cisco equipment, such as model numbers, IP addresses, and interface details. CDP is widely used for troubleshooting and maintaining Cisco networks.
- What is subnetting?
Subnetting is the process of dividing a large network into smaller sub-networks. It improves performance and simplifies management. Subnetting helps allocate IP addresses efficiently and reduces broadcast traffic. For example, a /24 network can be split into four /26 subnets for different departments.
CCNA Interview Questions for Freshers
These CCNA interview questions and answers are designed to help freshers understand the basics and prepare for entry-level networking roles.
- What are the layers of the OSI model?
The OSI model has seven layers. They are Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. Each layer has a defined role.
For example, the Network layer handles routing, while the Application layer interacts directly with users. This model helps standardize networking concepts across vendors.
- What is a default gateway?
A default gateway is a device, usually a router, that connects a local network to other networks or the internet. When a device cannot find a destination within its subnet, it sends the traffic to the default gateway, which routes it appropriately.
- What is DHCP, and how does it work?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns IP addresses and network configurations to devices.
It follows the DORA process: Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge. This saves administrators from manually assigning IP addresses and helps avoid conflicts.
- What is ARP?
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) maps an IP address to a MAC address in a local network. For example, when a PC wants to communicate within the LAN, ARP finds the hardware address of the destination device. The result is stored in the ARP table.
- What is OSPF, and how does it work?
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a link-state routing protocol. It uses the Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the shortest path for packets. Routers share link-state advertisements to build a network map, allowing fast and reliable route selection.
CCNA Interview Questions for Experienced
Let’s go through some important CCNA interview questions and answers for experienced professionals.
- What is EIGRP?
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is an advanced distance-vector protocol created by Cisco. It is used for exchanging routing information within an autonomous system. EIGRP relies on the DUAL (Diffusing Update Algorithm) to find the shortest path.
It uses metrics such as bandwidth, delay, reliability, and load. EIGRP supports fast convergence and is considered more efficient than RIP, while being less resource-intensive than OSPF.
- What is the difference between static and dynamic routing?
Static routing requires manual configuration of routes by an administrator. It is predictable but not scalable for large networks.
Dynamic routing, on the other hand, automatically updates routes using protocols such as OSPF, EIGRP, or BGP. Dynamic routing adapts to changes like link failures, while static routes stay fixed unless updated manually.
- What is NAT and its common types?
NAT (Network Address Translation) maps private IP addresses to public ones, allowing multiple devices on a LAN to share limited public IPs. It improves security by hiding internal addresses.
Common types include Static NAT (one-to-one mapping), Dynamic NAT (automatic assignment from a pool), and PAT (Port Address Translation), where many private IPs share one public IP using port numbers.
- What is BGP, and how does it work?
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is the protocol that runs the internet. It is a path-vector protocol used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems.
BGP chooses routes based on attributes like AS path, next-hop, and policy rules rather than just metrics. Internet service providers and large enterprises rely on BGP for external routing.
- What is the role of RSTP?
RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) is an improvement over STP. It reduces convergence time from about 30–50 seconds to less than 10 seconds. RSTP achieves this by introducing new port roles and faster state transitions, making switched networks more resilient and responsive.
Note: CCNA job interview questions often include both theoretical concepts and practical scenarios to test your networking knowledge. So, let’s take a look at some scenario-based questions.
CCNA Scenario Based Interview Questions
Here are practical CCNA scenario based questions and answers that test how you apply networking knowledge to solve problems.
- A user cannot connect to the internet while others can—how would you troubleshoot?
I would first check the physical connection, like cables or Wi-Fi. Then I would confirm the user’s IP configuration with ipconfig or ifconfig. If the IP address or gateway is missing, I would test DHCP assignment.
Next, I would ping the gateway to confirm local connectivity. If that works, I would test external reachability using ping 8.8.8.8. Finally, I would check DNS by pinging a domain like google.com.
- Which devices can be configured as a default gateway in a LAN?
Routers are most commonly used as default gateways. They connect internal networks to external networks and direct outbound traffic. Layer 3 switches can also act as default gateways in larger LANs because they support routing functions. In smaller setups, firewalls can serve as gateways too, handling both routing and security policies.
- What is the role of ARP in a LAN scenario?
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) resolves IP addresses to MAC addresses within the same LAN. When a device wants to send data to another device on the network, it uses ARP to find the destination’s hardware address. Without ARP, IP communication inside a local subnet would not be possible.
- How would you identify and prevent routing loops?
Routing loops can be spotted when packets keep circulating without reaching their destination. To prevent them, protocols like RIP use split horizon and route poisoning.
OSPF and EIGRP avoid loops through topology databases and DUAL. Properly setting maximum hop counts also protects against endless looping.
Cisco Switching Interview Questions
Now, let’s explore some key Cisco switching interview questions and answers that are commonly asked to test switching concepts and configurations.
- Explain the difference between a router and a switch.
A switch operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model. It connects devices within the same network and forwards frames based on MAC addresses. A router operates at Layer 3.
It connects different networks and forwards packets based on IP addresses. In short, switches handle local communication, while routers handle traffic between networks.
- What are VLANs and why are they used?
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical segmentation of a switch into separate broadcast domains. VLANs improve security, reduce broadcast traffic, and make networks easier to manage.
For example, HR and Finance teams can be placed in separate VLANs even if they use the same physical switch.
- What is STP and how does it prevent loops?
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) prevents switching loops in redundant topologies. It does this by blocking certain paths and allowing only one active path between switches. If a link fails, STP recalculates and activates a backup path. This avoids broadcast storms and keeps the network stable.
CCNA Networking Interview Questions
You might also find these CCNA interview questions with answers helpful for strengthening your core networking knowledge and interview preparation.
- What are the two types of IP addresses?
There are two main types: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 uses 32 bits, giving about 4.3 billion addresses. IPv6 uses 128 bits, offering a nearly unlimited number of addresses. IPv6 was developed to solve IPv4 exhaustion and also includes improved features for security and efficiency.
- What is the difference between a public IP and a private IP?
A public IP is assigned by an ISP and is used to communicate over the internet. A private IP is used within local networks and cannot be routed on the internet directly.
For example, 192.168.1.10 is a private IP, while 203.x.x.x would be a public IP. Public IPs require global uniqueness, while private IPs can be reused across multiple LANs.
- What is the OSI model and why does it matter?
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model has seven layers. It matters because it standardizes how systems communicate, making troubleshooting easier. Each layer, from Physical to Application, has specific tasks. For instance, the Transport layer ensures reliable data delivery.
- What is network congestion and how can you mitigate it?
Network congestion happens when demand exceeds available bandwidth. It causes packet loss, delay, and poor performance. To reduce it, admins may segment networks with VLANs, use QoS (Quality of Service), upgrade bandwidth, or optimize routing paths.
CCNA CCNP Interview Questions
This section covers important CCNA CCNP interview questions and answers that help you prepare for both associate and professional-level networking roles.
- What is HSRP and why is it used?
HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) is a Cisco protocol used for gateway redundancy. It allows two or more routers to work together, with one acting as active and the other as standby. If the active router fails, the standby takes over instantly. This provides continuous availability for network users.
- What is the difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches?
A Layer 2 switch forwards frames using MAC addresses. It is used mainly for local area communication. A Layer 3 switch can perform both switching and routing.
It makes forwarding decisions using IP addresses and supports inter-VLAN routing. In short, Layer 3 switches combine the functions of a router and a switch.
- What is IS-IS routing protocol?
IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System) is a link-state routing protocol. It is widely used in service provider environments. IS-IS builds a full topology map of the network and uses the shortest path first algorithm for routing. It supports IPv4 and IPv6.
- What is the function of IPsec?
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) is a suite of protocols that secures IP traffic. It provides authentication, integrity, and encryption. IPsec is commonly used in VPNs to protect data traveling across public networks.
Also Read - Top 20+ Network Security Interview Questions and Answers
Tips to Prepare for CCNA Interview Questions
Here are some practical tips to help you prepare for CCNA interview:
- Study core CCNA interview topics like OSI model, routing, VLANs, and subnetting
- Practice answering CCNA job interview questions in a clear and structured way
- Set up a small lab with Packet Tracer or GNS3 to test concepts
- Revise commands for routers and switches
- Focus on real troubleshooting examples, not just theory
Wrapping Up
With these 25+ CCNA interview questions and answers, you can approach your next interview with confidence. From basic networking concepts to advanced routing and switching, these questions cover what matters most.
Looking for IT job opportunities? Visit Hirist to find top IT roles, including CCNA jobs.
FAQs
Common CCNA interview topics include OSI model, subnetting, IP addressing, VLANs, routing protocols, NAT, DHCP, and troubleshooting.
Here are the common advanced questions:
How does BGP select the best path?
What is the difference between RSTP and STP?
How does EIGRP calculate its metric?
Explain the role of VRF in MPLS networks.
How does OSPF handle area design in large networks?
They can be challenging for beginners, but with proper study and hands-on practice, they are manageable.
Revise fundamentals, practice lab scenarios, and be confident while explaining solutions. Hands-on experience helps the most.
According to AmbitionBox, a Network Engineer with CCNA certification in India earns an average annual salary of around ₹4.6 Lakhs. The pay ranges between ₹2 Lakhs to ₹7 Lakhs for professionals with 1–6 years of experience. The typical monthly in-hand salary is about ₹34,000 to ₹36,000.
Network Engineer CCNA Certified salary overview
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual salary range | ₹2 Lakhs – ₹7 Lakhs |
| Avg. annual salary | ₹4.6 Lakhs |
| Monthly in-hand salary | ₹34,000 – ₹36,000 |
| Experience range shown | 1 – 6 years |
Salary by experience
| Experience | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| 1 year | ₹3.8 Lakhs per year |
| 2 years | ₹4.0 Lakhs per year |
| 3 years | ₹4.3 Lakhs per year |
| 4 years | ₹4.5 Lakhs per year |
Salary by city
| City | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Pune | ₹7.0 Lakhs per year |
| New Delhi | ₹4.2 Lakhs per year |
| Mumbai | ₹4.2 Lakhs per year |
| Navi Mumbai | ₹3.1 Lakhs per year |
| Bhopal | ₹3.0 Lakhs per year |
Top companies like Cisco, TCS, Wipro, Infosys, HCL, Accenture, and global MNCs regularly hire CCNA-certified candidates.

